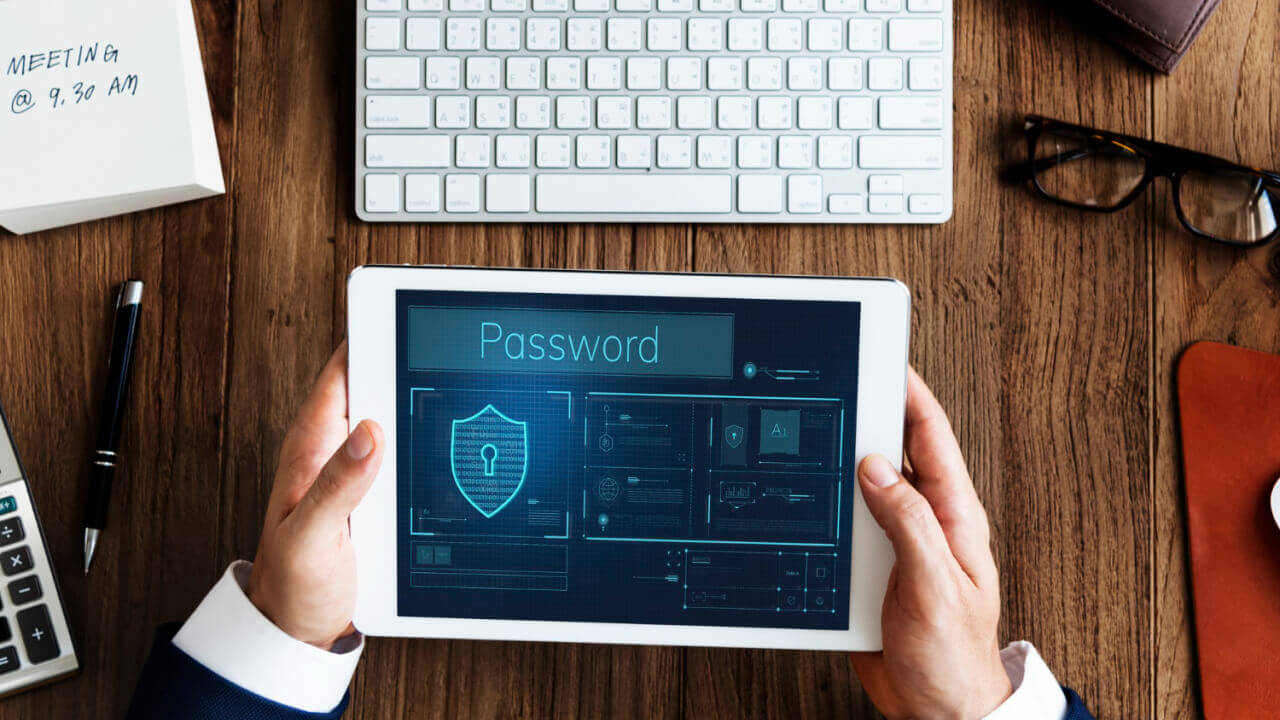
Passwords have long been the cornerstone of digital security, but their time may finally be up. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the difficulty of managing multiple complex passwords, the need for a safer and more user-friendly solution has become urgent. The future of authentication is passwordless, and it’s already here.
The End of Passwords: Why the Shift is Necessary
In recent years, passwords have proven to be more of a liability than a solution. For instance, a breach involving MyFitnessPal exposed the encrypted passwords of approximately 150 million users, underscoring the vulnerabilities inherent in traditional authentication methods often encountered in login forms across various websites.
While passwords were once a reliable safeguard, they often serve as the weakest link in a security chain. Hackers exploit phishing scams, brute-force attacks, and credential stuffing to gain unauthorized access, leaving consumers and businesses at risk.
Beyond security, the user experience with passwords could be more convenient. Managing numerous unique and complex passwords often leads to bad practices like reusing or storing passwords insecurely. According to Private Internet Access (PIA), it’s clear that the way forward lies in eliminating passwords and adopting more secure methods.
Zero Login: Redefining Authentication
Zero login, a revolutionary approach to authentication, is already gaining traction. It leverages advanced technologies to verify a user’s identity without requiring them to actively login. Instead of relying on passwords, it uses behavioral biometrics, contextual data, and device interactions to ensure secure access.
How Zero Login Works
Zero login technologies analyze intricate and unique behavioral characteristics, such as:
- Typing Patterns: The speed and rhythm of typing.
- Pressure Sensitivity: The force applied to a touchscreen.
- Environmental Factors: Location, device usage, or connected peripherals like headphones.
These technologies create an almost impossible-to-replicate security profile, making it more secure and seamless than traditional authentication methods. For example, modern iPhones can remember signals from devices like your car or smartwatch, continuously validating your identity based on contextual factors.
These systems offer robust protection while enhancing convenience, as users no longer need to enter passwords for every transaction.
Real-world Examples of Zero Login in Action
You may have already experienced zero login without realizing it. Numerous websites, especially in sectors like online banking, track user activity and may request verification if they detect unusual behavior, such as logging in from a different location.
Tech giants like Amazon are exploring behavioral authentication methods, using data like typing speed and screen pressure to verify identities. Similarly, Apple’s iPhone integrates biometric features that work seamlessly with other connected devices, creating a secure and unified ecosystem.
Benefits of a Passwordless Future
The shift to zero login and passwordless systems is more than just a trend—it’s necessary. Here’s why:
- Enhanced Security: Passwordless systems eliminate vulnerabilities like weak or stolen passwords, making it exponentially harder for attackers to breach accounts. Advanced behavioral data is unique to each user, creating an additional layer of defense.
- Improved User Experience: With zero login, users can enjoy frictionless access to their devices and applications without the hassle of remembering and entering passwords. This convenience boosts engagement and satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs for Businesses: Managing password resets and IT support for account recovery is costly. Organizations can save time and resources by adopting passwordless technologies while providing better security.
Challenges of Zero Login
While the benefits are undeniable, the transition to zero login raises several concerns:
Privacy and Data Security
Collecting and storing behavioral data, biometrics, and location information introduces privacy risks. If this sensitive data is transmitted to the cloud for analysis, robust encryption, and security protocols are essential to prevent misuse. To mitigate this risk, technologies are evolving to store behavioral data locally on devices whenever possible, minimizing exposure to potential breaches.
Constant Monitoring
Passive authentication could mean users are always logged into their accounts, sometimes without realizing it. If devices are not properly secured, this could lead to accidental access or unauthorized activity. For example, if a device is left unattended and unlocked, unauthorized access is risky. Continuous improvements in device security and session management are needed to ensure these systems do not inadvertently create new vulnerabilities.
Regulation and Consent
Governments and organizations must enforce regulations prioritizing user privacy and consent to ensure a successful transition. Transparency about how data is collected, used, and stored is crucial. Clear consent mechanisms will help users feel more comfortable about the data being collected, and organizations must adhere to stringent privacy standards to maintain trust.
A Balanced Approach to Zero Login
To truly perfect zero login, it must strike a balance between security, convenience, and privacy. Here’s how:
- Encryption and Secure Storage: Behavioral data and biometrics should be stored locally on devices whenever possible, minimizing exposure to potential breaches. Encryption should be robust to protect user privacy when data must be stored remotely.
- User Control and Consent: Users should have control over what data is collected and how it is used, with clear opt-in options and privacy settings. Consent should be transparent and easy for users to manage.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) as a Backup: While zero login is designed to eliminate passwords, incorporating MFA as a fallback ensures additional protection in case of unusual activity. For example, an email or phone number-based verification can be a secondary authentication layer in sensitive scenarios.
The Path Forward: Building Trust in Passwordless Systems
Adopting passwordless authentication is not just about technology but about building trust. Educating users on the benefits and addressing their concerns will be critical for widespread acceptance. As zero login technology evolves, the focus must remain on creating a seamless experience without compromising security or privacy. Regulations, transparent practices, and continuous innovation will help achieve this balance.
Conclusion: A New Era of Authentication
The future of authentication is here, and it’s passwordless. By leveraging technologies like behavioral biometrics, device-based authentication, and environmental data, zero login is poised to redefine how we secure our digital lives.
While challenges remain, the advantages of improved security, better user experiences, and cost efficiency make this transition inevitable. As we move forward, perfecting these systems and addressing privacy concerns will ensure that the new era of authentication is secure, frictionless, and trustworthy.
Say goodbye to forgotten passwords and hello to a smarter, safer way to access your world.
If you found this blog post helpful, don’t hesitate to share it with others. Let’s spread the word about the benefits of passwordless authentication for a safer and more convenient digital experience.